| New York State Social Studies Framework Key Idea & Practices | 12.E3 THE IMPACTS OF AMERICAN CAPITALISM IN A GLOBAL ECONOMY: There are various economic systems in the world. The United States operates within a mixed free market economy characterized by competition and a limited role of government in economic affairs. Economic policy makers face considerable challenges within a capitalist system, including unemployment, inflation, poverty, and environmental impact. Globalization increases the complexity of these challenges significantly and has exerted strong and transformative effects on workers and entrepreneurs in the US economy. In addition , this inquiry highlights the following Conceptual Understandings:
|
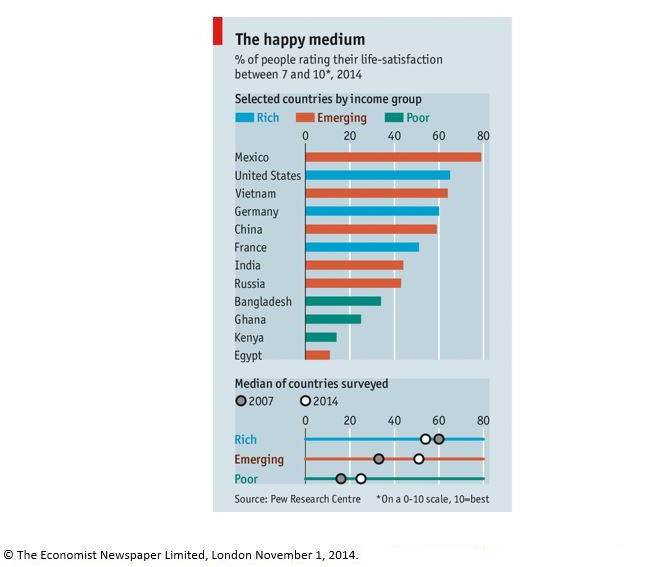
| Staging the Question | Analyze the graph “The Happy Medium” and discuss whether money can buy happiness. Teachers could use this discussion as a bridge to talk about the growing trend of assessing happiness through economic measures and the fact that this inquiry looks at several different ways of doing that, each of which produces very different results. |
Supporting Question 1- Why do some consider Denmark the happiest country in the world?
The first supporting question—“Why do some consider Denmark the happiest country in the world?”—helps students explore the reasons Denmark ranks number one on the 2013 World Happiness Report and the factors that influence a country’s ranking according to this particular measure. The formative performance task calls on students to list the reasons for Denmark’s ranking by examining sources featuring aspects of the Danish economic system and the choice Danes make to pay higher taxes for greater public security. The featured sources include a breakdown of economic factors such as housing, income, jobs, education, and health care as well as other happiness factors such as community engagement, work-life balance, and life satisfaction.
- Featured Source: Graph representing survey on happiness, “Everything that rises must converge” (excerpt), The Economist, November 1, 2014
Source A: John Helliwell, Richard Layard, and Jeffrey Sachs, international rankings of happiness, “Rankings of Happiness 2010-2012,” World Happiness Report (excerpt), 2013 NOTE: The World Happiness Report data used in Supporting Questions 1 and 2 examines public policy shifts amongst nations of the world. In order to do this, the authors of the report measure happiness as how efficiently countries provide a good quality life to their citizens while limiting the amount of environmental resources used. In other words, happiness is not defined as an emotion, but rather as a “life satisfaction.” The data supports the argument that wellbeing and sustainable development should be integral in countries’ public policy moving forward. The chart used as a source in this inquiry is based on averages from data collected from 2010–2012.- Source B: Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), report on life factors in Denmark, Denmark Better Life Index (excerpt), 2014
For the second supporting question—“How does the United States rank in happiness?”—students build on their understanding of the World Happiness Report by analyzing two additional studies that rank the United States using very different metrics. The formative performance task for this supporting question requires students to create a three-column chart that reflects the three studies, and to list the United States rankings in each study and the reasons for those rankings. For example, the United States ranks number 17 on the 2013 World Happiness Report, number 12 on the 2014 Economic Freedom of the World Report, and number 104 on the 2015 Happy Planet Index. Students should consider the metrics used to generate the rankings (e.g., the Economic Freedom of the World Report uses size of government, free trade, and number of business regulations) and how the reports reflect very different economic values—security, freedom, and global sustainability, respectively.
- Source A: John Helliwell, Richard Layard, and Jeffrey Sachs, international rankings of happiness, “Rankings of Happiness 2010-2012,” World Happiness Report (excerpt), 2013
NOTE: Refer to Supporting Question 1, Featured Source A: World Happiness Report, © 2013 United Nations. http://unsdsn.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/02/WorldHappinessReport2013_online.pdf. - Source B: Fraser Institute, international rankings of economic factors, Economic Freedom of the World (excerpt), 2014
The full report can be found online at: http://www.freetheworld.com/2014/EFW2014-POST.pdf
Courtesy of The Fraser Institute, www.freetheworld.com. Used with permission.
Courtesy of The Fraser Institute, www.freetheworld.com. Used with permission.
- Source C: New Economic Foundation, international ranking of economic factors, Happy Planet Index Results (excerpt), 2014. The Happy Planet Index (HPI) measures what matters: the extent to which 151 countries deliver long, happy, sustainable lives for the people that live in them. The Index uses global data on life expectancy, experienced well-being and Ecological Footprint to calculate this.
The index is an efficiency measure, it ranks countries on how many long and happy lives they produce per unit of environmental input.
Having examined how different organizations measure a country’s economic happiness and how and why the United States ranks as it does, students answer the third supporting question—“What economic policies could make Americans happier?” The formative performance task requires that students address the supporting question by developing a claim supported with evidence. The featured sources for this task include the political platforms from the Republican, Democratic, and Green parties, all of which include both broad and specific policy directions aimed at creating greater prosperity and thus, in their own way, greater happiness.
- Source A: Republican Party, statement of party economic beliefs, Republican Party Platform: Restoring the American Dream and Jobs (excerpts), 2012 Courtesy of Republication National Committee. https://www.gop.com/platform/restoring-the-american-dream/. Used with permission.
- Source B: Democratic Party, statement of party economic beliefs, Democratic Party Platform: Moving America Forward (excerpt), 2012 Courtesy of The American Presidency Project. http://www.presidency.ucsb.edu/. Used with Permission.
- Source C: Green Party, statement of party economic beliefs, Green Party Platform: Economic Justice and Sustainability (excerpt), 2012.